Understanding Ocular Hypertension and the Need for Treatment
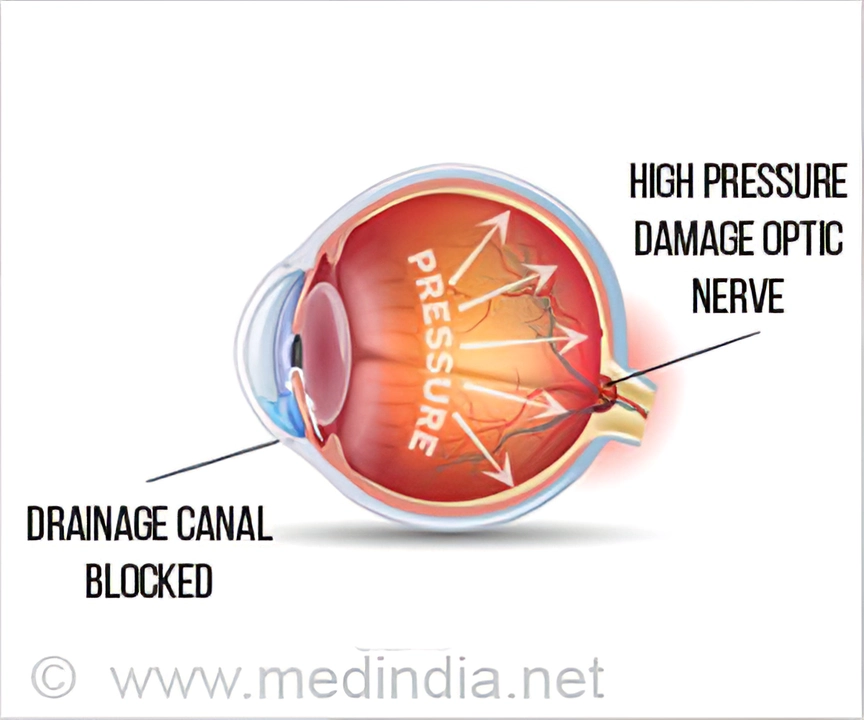
Ocular hypertension, a condition where the pressure inside the eye is higher than normal, can lead to serious eye problems if left untreated. It's important to understand the risks and potential complications associated with this condition. In this article, we will explore the role of brinzolamide in treating ocular hypertension, examining how it works, its benefits, and potential side effects.
How Brinzolamide Helps Lower Intraocular Pressure
Brinzolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor that works by reducing the production of aqueous humor, the fluid inside the eye. This, in turn, helps to lower intraocular pressure. By maintaining a healthy eye pressure, brinzolamide can help prevent damage to the optic nerve, which could lead to vision loss or even blindness.
Proper Use and Dosage of Brinzolamide
Brinzolamide comes in the form of eye drops, and the proper use and dosage are crucial for achieving the desired results. It is important to follow your doctor's instructions carefully when using this medication. Typically, brinzolamide eye drops are applied to the affected eye(s) two to three times daily. Make sure to wash your hands before and after applying the eye drops, and avoid touching the dropper tip to prevent contamination.
Combining Brinzolamide with Other Glaucoma Medications
In some cases, brinzolamide may be prescribed in combination with other glaucoma medications to effectively manage ocular hypertension. It is important to discuss with your doctor the other medications you are taking, as certain combinations may not be recommended. Always follow your doctor's instructions and do not alter your medication regimen without consulting them first.
Benefits of Brinzolamide Treatment
There are several benefits to using brinzolamide for the treatment of ocular hypertension. First and foremost, it effectively lowers intraocular pressure, which can help prevent vision loss and other complications. Additionally, brinzolamide has been shown to have fewer side effects compared to other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, making it a more tolerable option for many patients. Finally, its convenient dosing schedule of two to three times daily makes it an easy-to-follow treatment option.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
As with any medication, there are potential side effects to be aware of when using brinzolamide. Some common side effects include burning or stinging sensations in the eye, blurred vision, and a bitter taste in the mouth. More serious side effects, though rare, can include eye pain, severe redness or swelling, and signs of an allergic reaction. If you experience any of these more serious side effects, contact your doctor immediately.
Conclusion: The Importance of Early Intervention
In conclusion, brinzolamide plays a crucial role in the treatment of ocular hypertension by effectively lowering intraocular pressure and preventing potential complications. It is essential to follow your doctor's instructions closely and to report any side effects or concerns promptly. By staying vigilant and proactive in your eye care, you can help preserve your vision and maintain a high quality of life.

 Health and Wellness
Health and Wellness
Noah Seidman
April 27, 2023 AT 19:48We must treat ocular hypertension not as a ticking time bomb but as a moral imperative to protect vision. Brinzolamide, with its carbonic anhydrase inhibition, is a rational choice that respects the sanctity of the eye. Yet many patients ignore the regimen, believing the eye will somehow heal itself-an attitude born of hubris. The responsibility lies with both doctor and patient to enforce disciplined adherence.
Anastasia Petryankina
May 1, 2023 AT 08:54Ah, because nothing screams 'cutting‑edge pharmacology' quite like a drop that tastes like pennies. One can only imagine the elite circles where brinzolamide is debated over vintage wines, while the rest of us merely squint at our ophthalmologists' pamphlets.
Tim Ferguson
May 4, 2023 AT 21:59Brinzolamide is a drop that lowers eye pressure by stopping the eye from making too much fluid. It works by blocking an enzyme called carbonic anhydrase, which normally helps create the watery part of the eye. When the enzyme is blocked, less fluid is produced and the pressure goes down. Lower pressure means the optic nerve is safer from damage. This drug is taken two or three times a day, as the article says. The schedule may seem many drops, but it is easier than a surgery. Some people feel a sting when they put the drops in, but that feeling fades. The taste can be bitter, like metal, but it does not stay in the mouth for long. It is important not to touch the tip of the bottle to the eye, because germs can get in. If you get a rash or your eye hurts a lot, you should call the doctor right away. The side effects are usually mild, but serious reactions can happen rarely. Parents should watch kids carefully, because kids may not tell you they feel weird. The drug can be used with other glaucoma medicines, but the doctor must approve the mix. Do not stop using the drops without checking with a professional, even if you feel fine. Keeping the eye pressure low is the best way to avoid blindness in the future.
Noah Cokelaere
May 8, 2023 AT 11:05So while you're cataloguing every drop like a grocery list, remember the eye also enjoys a little mystery-maybe a drop now and then just to keep the doctor guessing.
Ashley Helton
May 12, 2023 AT 00:10Great, now we all have a new excuse to avoid eye exams-thanks, brinzolamide!
Brian Jones
May 15, 2023 AT 13:16Indeed-remember, consistency is key!!! Even if the drops feel like a tiny sting, they are your ally; adhere faithfully, and you’ll keep your vision sharp!!
Carlise Pretorius
May 19, 2023 AT 02:21yeah i dunno if i can keep up with 2-3 drops a day but i guess its better than lose my sight lol
Johnson Elijah
May 22, 2023 AT 15:27👁️💧Let's give a round of applause for brinzolamide-keeping our peepers pressure‑free, one drop at a time! 🌟
Roxanne Lemire
May 26, 2023 AT 04:32If we consider vision as a window to the world then each drop is a quiet sentinel guarding that pane
Alex Mitchell
May 29, 2023 AT 17:37Exactly-small actions, big impact :) stay consistent and the eyes will thank you
Narayan Iyer
June 2, 2023 AT 06:43From a clinical pharmacology standpoint, the synergistic modulation of aqueous humor dynamics by brinzolamide, especially when integrated into a multi‑agent regimen, exemplifies a paradigm shift in ocular hypertension management-think of it as a terabyte of data compressed into a single micro‑dose.